Last updated on April 26th, 2024
Watermelon does comprise natural sugars. Watermelon is classically a summertime preferred choice. Even though when you wish to plate some of the delicacies at every meal, or wish to make a normal summer snack, it’s always a good idea to check the product label first for its nutritional levels. If any person has diabetes, it becomes very important for him or her to track the diet pattern and also blood glucose levels. Based upon the person’s overall diet and how much watermelon he or she has consumed, this may affect the blood glucose levels. Read further to know more about how much sugar a watermelon contains and how it affects people with diabetes.

Watermelon, a Revitalizing Summer Fruit
On a hot sunny day, people may think: what can be anything better than having a thick slice of cold watermelon? Watermelon just can’t be beaten when it comes to refreshment. It is such a fan following or much-beloved one that it even has its special day which is, August 3 (National Watermelon Day). Can there be any better time to have fun by gulping this thirst-quenching fruit!
Watermelon has become an icon of summer as per the traditions. It is energizing, bright, and contains more than 90% water, consequently the name. Watermelon is referred to as a pepo: a modified berry having a rough and thick outer rind. It is heavily measured as a melon, though it doesn’t belong to the Cucumis genus. It belongs to the same Cucurbitaceae family as melons, pumpkins, or cucumbers.
Any diabetic person may be a bit hesitant about consuming watermelon. Nevertheless, watermelon is one of the most loved fruits containing natural sugar. So, can sugar patients eat watermelon? How can a watermelon influence your blood glucose levels? And tastiness kept sideways, is it a healthy food to have? Read on!
Also Read: Can Diabetics Eat Mango? | Know About Mango Glycemic Index & Nutritional Facts

Watermelon: Fruit or Vegetable?
It doesn’t matter to a majority of people whether watermelon is a fruit or a veggie, their main focus is to dig in and have the benefit of fruit. But if anyone believes in facts, then he or she might be fascinated to find out that watermelon is both a fruit and a veggie.
The reason is: botanically, watermelon is a fruit, identical to pumpkins or tomatoes (being fruits). Also, watermelon belongs to the plant family, Cucurbitaceae (family of gourds; other members being pumpkin or cucumber). And just like other veggies, they can be grown well in the gardens. So, yes, watermelon can be counted as a vegetable.
Also Read: Sugar Test Price
Watermelon Benefits
- The summer fruit is an incredible source of minerals and vitamins including Vitamin C, A, B6, potassium, iron, magnesium, calcium, and fibers.
- Vitamin A promotes healthy vision and helps in the upkeep of your heart, kidneys, and lungs.
- Vitamin C is also beneficial for a healthy diet and helps to improve heart health, defeat the signs of the common cold, and prevent certain cancers.
- Also, as the fruit is rich in fiber content, its intake supports good digestive health.
- When moderate amounts of watermelon are taken, it curbs people’s craving for something sweet, along with keeping the tummy full for a longer period. This is because watermelon is above 90% water.
- Along with keeping the person hydrated, watermelon considerably helps in weight management.
- The fruit also diminishes the risk of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.
- Watermelon is very good for skin and hair health as well.
Also Read: Is Walnut Good For Diabetes? | Check Glycemic Index of Walnuts
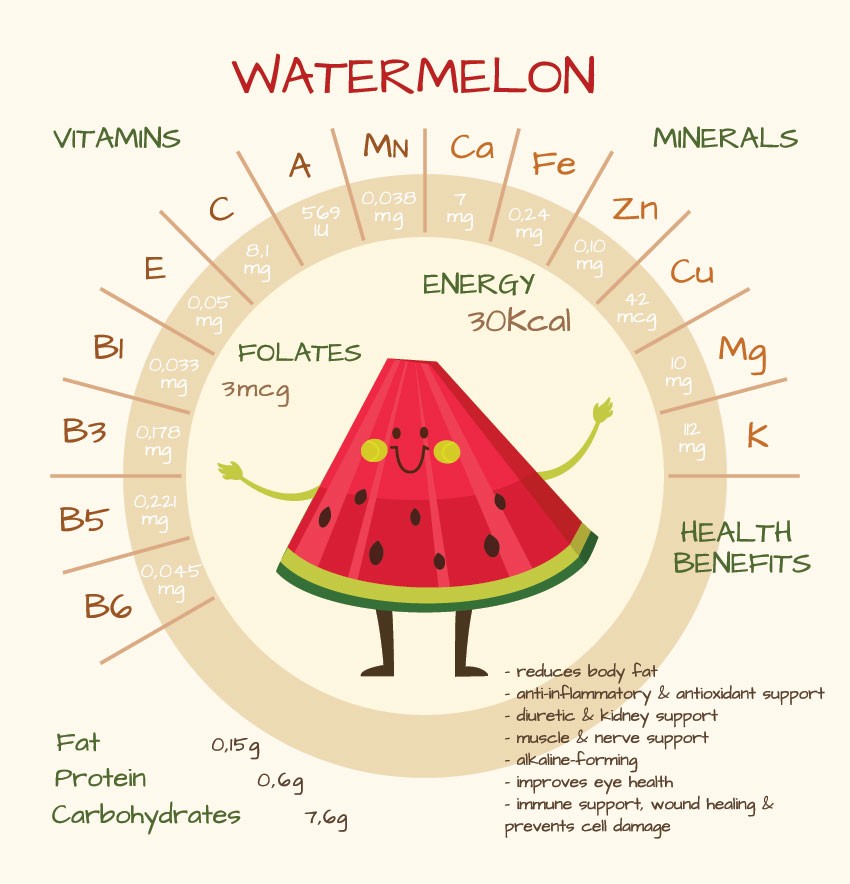
Watermelon Nutrition
Every part of a watermelon is edible and can be consumed; thereby it is well thought-out as a zero-waste food. Watermelon rind and seeds contain diverse nutritional values than the inside of the fruit. Many studies have found a significant usage of watermelon seeds for diabetes. Often the seeds are roasted and the rind can be utilized as a veggie, can be pickled, or fried as well.
Macronutrients and Calories
Water constitutes about 92% of the watermelon’s weight. Carbs are the chief macronutrient present in it. Watermelon has a very low concentration of proteins, with only 0.6 grams of proteins in 100 grams of watermelon. In addition, it has a number of fats, thus it has low amounts of saturated fats and no trans fats or cholesterol. 100 grams of watermelon is composed of only 30 calories.
Roughly, watermelon seeds are composed of higher amounts of protein (8%) and fats (17%), together with fiber (40%) and calories. The rind of this fruit is very rich in a non-essential amino acid named citrulline, which is also found in the flesh.
Also Read: Bigomet SR 500 Tablet For Diabetes: Uses, Side Effects, Dosage & Interactions
Vitamins
Watermelon is an exclusive source of vitamins A and C. Also, it comprises low to moderate amounts of vitamin B complex, especially vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, and B6. It has a low amount of vitamin K and E. Vitamins D, B12, and B9 are completely absent in this fruit.
Watermelon seeds contain rich amounts of vitamins E and C. Also, they have a much higher content of vitamin B3 than the flesh. The rind is richer in vitamin A and vitamin C.
Minerals
The pulp of a watermelon is found to be rich in minerals like calcium, potassium, magnesium, manganese, and phosphorus. Moderate quantities of iron, choline, selenium, copper, and zinc are found; with low amounts of sodium. The seeds contain substantial minerals like sodium, calcium, zinc, phosphorus, magnesium, and potassium.
Read on to know about the association between watermelon and blood sugar!
Also Read: Can Quitting Smoking Reverses Diabetes?
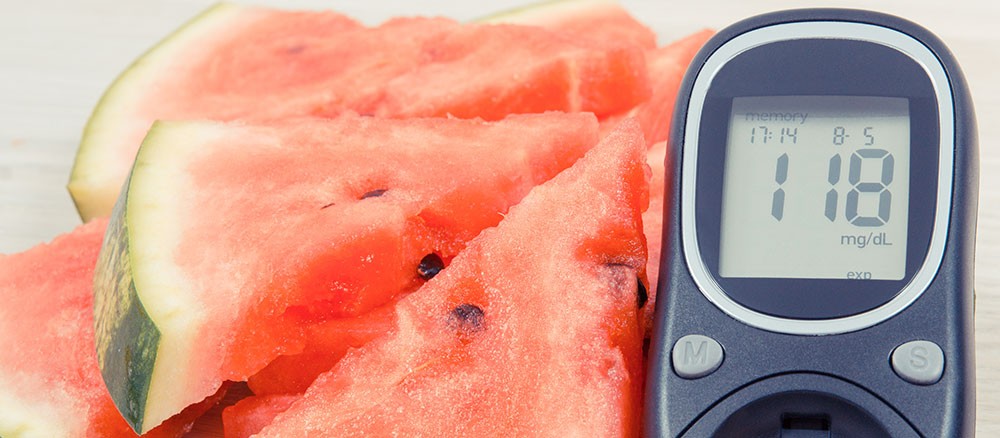
Watermelon Effect on Diabetes
Does watermelon cause diabetes? The answer is no. Consumption of watermelon greatly helps in lowering the risk for certain diabetes-associated complications. The fruit consists of moderate amounts of lycopene, a pigment offering watermelon its rich color. It is a powerful antioxidant. Lycopene also helps in decreasing the risk of certain cardiovascular disorders. Studies suggested that lycopene present in tomatoes is also directly related to a decreased risk for heart problems. About 68% of diabetics with age 65 years or older die from some kind of heart problem, and about 16% of these people die of stroke.
Diabetes is an ailment characterized by high levels of glucose in the blood. This can happen when the beta cells in the pancreas get damaged. These are responsible for the secretion of the hormone insulin, which helps control the blood glucose concentrations. On intensification of these blood sugar levels, many serious complications like eye damage, kidney failure, neuropathy, or heart problems can occur.
Does eating watermelon raise blood sugar levels? A small part of fresh-cut watermelons when consumed by diabetics (type 2) can benefit them in many ways. Even though melon glycemic index (GI) is 72, melon glycemic load (GL) is moderately lower i.e. 2 per 100 grams serving. Moreover, it also contains low amounts of calories and carbs, thus not adding to the accumulation of excess fat in the body tissues. This in turn helps in maintaining optimal body weight, which is nowadays very essential to improve the overall standard of living of people with diabetes.
Additionally, watermelon seeds, which individuals normally tend to throw away, can indeed be crushed, made into thin powder, and can be taken by diabetics. Watermelon seeds are a powerhouse of nutrients like omega 3s, omega 6, proteins, potassium, zinc, and various vitamins.
Also Read: Is Pineapple beneficial for people with diabetes?
Is Watermelon Juice High in Sugar?
It is usually safe for people with type 2 diabetes to consume watermelon, drink the juice and gulp the seed extracts, remember in restricted proportions only. It’s good to check with the concerned doctor or nutritionist, so as to learn about the ideal way how one can add this juicy and tasty delight to a low-sugar diet. Also, this can depend upon the current status of blood glucose levels.
Summary
It is always recommended to have a well-balanced meal of a moderate portion of watermelons, either alone or in combination with other low glycemic index foods. This helps in keeping the blood sugar levels in check, for people with type 2 diabetes or prediabetes signs.
Where is Watermelon on the Glycemic Index Scale?
The Glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how fast food sugar goes into the bloodstream.
Each food product is ranked between 1 to 100. These values can be determined as per the comparison of each food item with the reference item. Here, the reference item can be sugar or white bread.
Glycemic load (GL) means summing up the GI and the actual carb content in any food serving. Foods having a low or medium GI are considered less expected to spike blood glucose levels.
- Low: GI 55 or less
- Medium: GI between 55 and 69
- High: Anything above 70
Also, GLs under 10 are low, 10 to 19 are medium, and 19 and over are considered high.
A classic example is the watermelon glycemic index of 72 along with a GL of 2 per 100-gram serving. The glycemic load of the fruit is low and can be consumed in moderation similar to all fruits as part of a balanced meal.
Also Read: Sliding scale insulin chart dosage
What are Some Other Diabetes-Friendly Fruits?
Even though the consumption of watermelon carries its benefits, any person must consider balancing his or her diet with fruits with a lower glycemic index. Make sure to pick up the fresh fruits available, as these don’t have any added sugars.
If any person wishes to purchase canned or frozen fruit, he or she must choose only the canned fruits packed in fruit juice or water, do not buy the syrupy ones. Thus, it’s very important to read the label vigilantly and try to find the hidden sugars. Dried fruits or fruit juices must not be preferred over fresh fruits. This is because of sugar concentration, calorie density, as well as smaller advisable portion sizes.
Diabetes-friendly fruits having a low GI can be pears, peaches, plums, berries, grapefruit, or apricots.
Summary
The juicy watermelon has a spectacular nutrient profile, overloaded with abundant water content and potent health-supporting compounds. Watermelon is naturally low in calories (sugar level of watermelon is insignificant), also offers plenty of vitamins A and C, on top of some very important trace minerals like iron, copper, or potassium. Also, watermelon is a rich source of the amino acid citrulline (which gets converted into arginine in the body) as well as the effective antioxidant lycopene.
The blast of constructive components inherently present in this summer fruit positively bestows the person with lots of beneficial traits. These can be lowering high blood pressure levels, reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications, hydrating the body, and healing muscle aches.
Also Read: Can glimepiride be taken with metformin?
FAQs:
Is watermelon a good detoxifier?
Is watermelon a good option for me if I want to lose my belly fat?
What must not be consumed with watermelon?
Does watermelon cause side effects?
What time of the day is not good for eating a watermelon?
References:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/diabetes/watermelon-and-diabetes#takeaway
- https://www.netmeds.com/health-library/post/is-watermelon-good-for-diabetes-incredible-health-benefits-of-this-refreshing-summer-fruit
- https://www.diabetesselfmanagement.com/healthy-living/nutrition-exercise/is-watermelon-good-for-diabetics/
- https://foodstruct.com/food/watermelon
Last Updated on by Dr. Damanjit Duggal
Disclaimer
This site provides educational content; however, it is not a substitute for professional medical guidance. Readers should consult their healthcare professional for personalised guidance. We work hard to provide accurate and helpful information. Your well-being is important to us, and we value your feedback. To learn more, visit our editorial policy page for details on our content guidelines and the content creation process.

 English
English