Hey there! With Ramadan right around the corner, Muslims everywhere are preparing for a month full of fasting, prayer, and self-reflection. But for those managing diabetes, this sacred time brings its own set of challenges. How do you fast Diabetes and Ramadan fasting while keeping your blood sugar levels in check? It’s a balancing act that requires some extra know-how and planning. In this blog, we’re diving into the world of diabetes and Ramadan fasting. We’ll talk about how fasting affects your body, share practical tips for meal planning and medication management, and much more. We will offer advice to help you make the most of this special time while taking care of your health. Whether you’re a newbie to diabetes or a seasoned pro at fasting during Ramadan, we’ve got your back with insights and strategies to help you navigate this journey safely and smoothly. Let’s dive in!

Psychological Effects of Fasting During Ramadan
The month of Ramadan involves fasting during the day. So, Ramadan fasting involves changes in eating and sleeping patterns. Since during the fast, you are not even allowed to intake fluids, including water, this affects your body differently. Also, for diabetic patients, Ramadan with diabetes leads to increased chances of both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. During Ramadan fasting, your body’s metabolism is affected by your changed eating and sleeping habits. So, these may affect your insulin production and insulin resistance levels along with glucagon levels. An EPIDIAR study published by the National Institute of Health revealed fasting in the month of Ramadan for diabetes patients increased the chances of hypoglycemia. In type 1 diabetics, it increased 4.7 times, and in type 2 diabetics, it increased 7.5 times.
Moreover, the same NIH-published study showed type 2 diabetic patients doing Ramadan fasting had a 5 times greater chance of increased blood glucose than others. Generally, it is seen many diabetes patients doing Ramadan fasting complain of a rise in their blood sugar. Therefore, it is important for diabetes patients planning to do Ramadan fasting to analyse the risk and consider present health conditions beforehand. People at higher risk should avoid fasting or limit it to specific days. Always consult with your diabetologist and discuss with them the possible precautions you can take.


Things to focus on for Diabetes and Ramadan

Following are the main areas a pre-Ramadan diabetes schooling should focus:
- Proper risk analysis.
- Regular blood glucose tests and constant monitoring.
- Adequate diet and fluid intake instructions.
- Exercising during Ramadan.
- Schedule of medicines for diabetes during Ramadan.
- Symptoms and situations to know when you must break the fast immediately.
Read More: 7 Day Indian Diet Plan for Diabetic Patients
Diet Management during Ramadan Fasting

Managing diabetes during Ramadan fasting requires careful planning and consideration. Here are some tips for dietary management during Ramadan fasting for diabetes patients:
Monitor blood sugar levels
Have a constant check on your blood sugar levels regularly, especially during fasting hours, to monitor for any fluctuations.
Suhoor/Sehri (pre-dawn meal)
Have a balanced Sehri meal that includes complex carbs, protein, and healthy fats to provide sustained energy throughout the day. Examples include atta roti, whole grain bread, lean protein (such as eggs or low-fat yogurt), and healthy fats (such as nuts or avocado).
Hydration
Drink plenty of water in the non-fasting hours to prevent dehydration. Along with this, avoid caffeine-rich and sugary drinks. These drinks can contribute to dehydration and fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
Iftar (breaking the fast)
Break your fast with a balanced meal that includes carbohydrates, protein, and vegetables. Avoid consuming large amounts of sugary or fried foods, as they can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
Portion control
It’s important for diabetics to be wary about the portion of food they consume. Avoid overeating during iftar, and suhoor will keep your blood sugar in control. Eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the night may help prevent blood sugar spikes.
Choose healthy cooking methods
Opt for baking, grilling, steaming, or roasting instead of frying when preparing meals. This can help reduce the amount of added fats and calories in your diet.
Include fibre-rich foods
Diabetics during Ramadan should incorporate meals full of fruits, veggies, whole grains, legumes, etc. These nutrients will help regulate their blood sugar.
Limit sweets and desserts
While it’s okay to enjoy sweets occasionally, limit your intake of sugary foods and desserts, as they can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
Remember to listen to your body and adjust your dietary plan as needed. If you experience any concerning symptoms or have difficulty managing your blood sugar levels, seek medical advice promptly.
Read More: Best Indian Diet Plan Chart for Weight Loss
Diet Plan for Diabetes in Ramadan

Following are the diet principles given which will help you during Ramadan:
- Your every meal should consist of 40% of complex carbs, 25-30% of protein and 30% of fat in total calories. However, saturated should be limited to less than 10%
- The carbs consumed should be complex and rich in dietary fiber. When consuming carbs, remember to pair them with fiber-rich veggies to eliminate any abrupt blood glucose fluctuations. Moreover, you should also limit the consumption of white or simple carbs like sugar, maida, etc.
- Maintain a healthy calorie intake range and divide calories evenly between sehri and iftar.
- Proteins with high saturated fats, like red meat, pork, beef, etc., should be avoided.
- Overweight diabetics should avoid weight loss diets during Ramadan fasting.
- Avoid consuming high-sugar food and drinks after iftar and sehri, or else your urge to drink water will increase.
- Consuming caffeinated beverages should be limited or best avoided.
- Your iftar should begin with plenty of water to overcome dehydration from fasting. Only then consume 2-3 dates to replenish blood sugar levels.
- Start your Sehri or Suhoor with a glass of methi water. Then wait for 15-20 minutes and take your sehri meal. The Methi water is a natural metabolism booster.
- Focus on consuming more protein and fats and lowering the carbs consumed in sehri.
- Take small snacks like nuts and low-GI fruits during the non-fasting hours.
- Avoid excessive salt in your food.
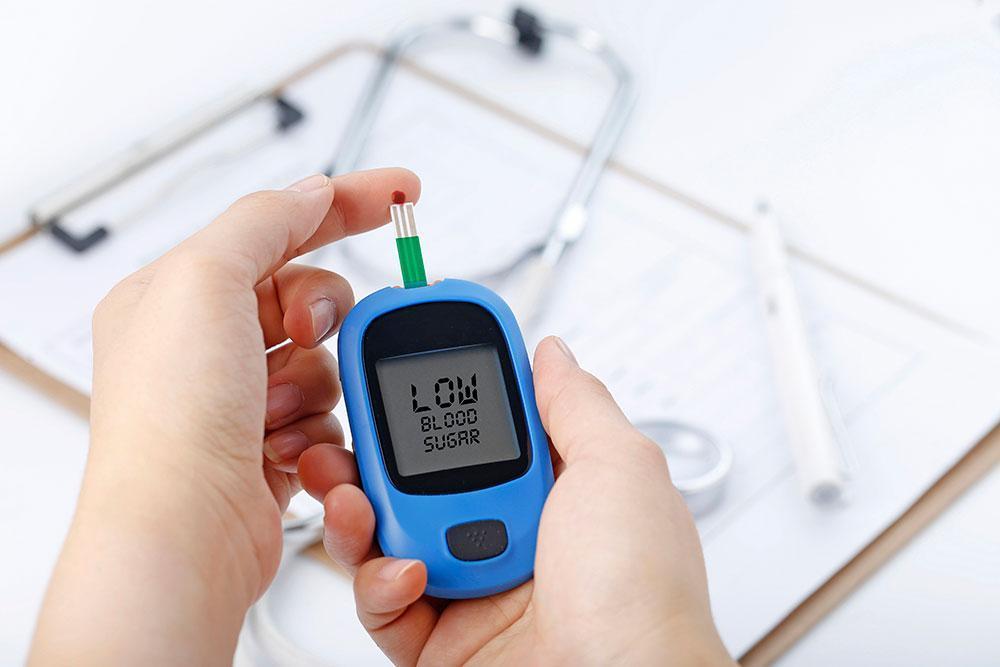
Importance of Blood Sugar Monitoring in Ramadan with Diabetes
Diabetes patients fasting during Ramadan should maintain a blood sugar monitoring schedule. The schedule will be a mix of self-monitoring blood sugar, continuous glucose blood sugar and lab tests. Maintaining this test schedule is very important as there are new changes in the pattern of your food and sleep. There are increased chances of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia during this period. Regular blood glucose monitoring will make sure your blood sugar stays in the safe range. It will also make you aware and conscious of your eating choices. The frequency of these tests may vary and fluctuate on diabetes type, present sugar levels and ongoing medications.
Read More: Is Rice Good For Diabetes?
Ramadan Workout Plan
Continuous fasting in the month of Ramadan brings some metabolic changes to your body. When fasting, your body uses the stored fats. However, studies have shown that continuous fasting for so long without any physical activity reduces physical strength and fitness. Therefore, doing physical workouts will enhance your strength and help you burn fat more efficiently. Consequently, we recommend doing some workout sessions regularly during Ramadan fasting.
Benefits of doing Workout or Gym during Ramadan
- Enhances the usage of stored fats, which is especially beneficial for overweight, diabetic patients.
- It helps in giving you better control of your blood glucose.
- Help you maintain your level of physical strength.
- Prevents breakdown of muscles.
- It makes you feel refreshed and less tired.
- It makes you more active during rituals and prayers.
Best Time of Workout during Ramadan
Before Iftar
- When doing gym during Ramadan, perform it 2 to 3 hours before iftar. However, only do light training to moderate training of 30 minutes when exercising before iftar.
- Perform exercising in an excellent space, preferably air-conditioned.
- Take sufficient fluids in the iftar to replenish salt and minerals.
After Iftar
- When performing a workout after iftar, do it after at least 2 to 3 hours.
- Perform exercise in an air-conditioned atmosphere.
Tips for Working Out while Fasting Ramadan
- Perform the Ramadan workout plan daily in a 30-45 min session.
- Avoid high-intensity weight training when doing a workout before iftar.
- Prefer doing exercise post iftar.
- Maintaining at least a 2 to 3-hour gap between meals and workouts.
- Doing jogging or walking in the Ramadan workout plan can also be done.
- Drink sufficient water to replenish minerals.
Read More: Top 6 Dry Fruits For Diabetics.
Taking Medicines for Diabetes in Ramadan
Diabetic patients taking medicines like insulin or sulfonylureas have increased chances of hypoglycemia. Therefore, diabetes patients should consult with their doctor/diabetologist before starting the fast. Moreover, maintaining a blood test schedule will help you regulate your blood sugar during fasting more efficiently.
Read More: Indian Diet for Diabetes Reversal.
Conclusion
As the sun sets on another Ramadan, it’s time to reflect on the journey we’ve taken, both spiritually and health-wise. For those managing diabetes, fasting during this holy month is not just about abstation from food and beverages. Ramadan is about finding harmony between our faith and health. Throughout this blog, we’ve explored the unique challenges and considerations that come with managing diabetes during Ramadan fasting. From understanding how fasting affects our bodies to practical tips for staying on top of blood sugar levels, we’ve covered a lot of ground. But perhaps the most important takeaway is this: your health should always come first. While fasting is a pillar of Ramadan, it’s not worth compromising your well-being. So, celebrate the holy Ramadan while keeping on your health. Ramadan Mubarak!! May your health and spirituality continue to flourish in the months ahead.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
According to research studies published by the National Institute of Health, diabetes patients having high A1c levels are strictly prohibited from fasting. However, diabetes patients with controlled HbA1c and sugar levels can fast only after a doctor’s consultation.
Following are steps diabetics need to take to manage diabetes during Ramadan:
Blood glucose monitoring
Proper diet and fluid intake during non-fasting hours
Discussing with your doctor about your fasting schedule
Avoid heavy workouts and work during the day.
According to the National Institute of Health, intermittent fasting is good for diabetics, especially overweight diabetic patients. However, before starting, the most important condition is that your blood sugar and A1c remain in the safe range.
Disclaimer
This site provides educational content; however, it is not a substitute for professional medical guidance. Readers should consult their healthcare professional for personalised guidance. We work hard to provide accurate and helpful information. Your well-being is important to us, and we value your feedback. To learn more, visit our editorial policy page for details on our content guidelines and the content creation process.

 English
English